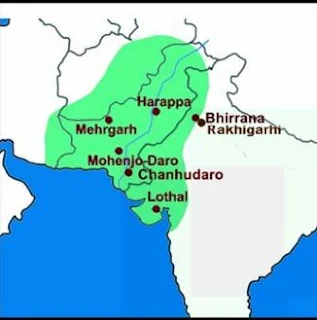
Harappan Civilization:
The Harappan Civilization, also known as the Indus Valley Civilization, was one of the world's earliest urban cultures, thriving in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from approximately 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE.
Here are key features and aspects of the Harappan Civilization:
1. Geographical Extent:
The Harappan Civilization covered a vast area, including parts of present-day India and Pakistan. Major sites include Harappa, Mohenjo-daro, Dholavira, and Kalibangan.
2. Urban Planning:
Cities of the Harappan Civilization were remarkably well-planned. Streets were laid out in a grid pattern, and buildings were constructed with standardized bricks, suggesting a high level of centralized planning.
3. Architecture:
Harappan cities featured advanced architectural techniques. Buildings were made of baked bricks, and structures like the Great Bath at Mohenjo-daro and the Granary at Harappa showcase their engineering skills.
4. Drainage System:
The cities had an efficient drainage system with well-laid-out brick-lined sewers. The Great Bath is thought to have been a part of a ritual or public bathing area.
5. Writing System:
The Harappan script is yet to be deciphered, and thus, the knowledge of their written records remains limited. Seals with inscriptions suggest a form of writing.
6. Trade and Economy:
The Harappans engaged in long-distance trade, evidenced by artifacts found at various sites. They had access to valuable resources like copper, tin, and semi-precious stones. The weights and measures discovered suggest a standardized system of trade.
7. Agriculture:
Agriculture was a crucial component of the Harappan economy. They cultivated wheat, barley, rice, and various other crops. The presence of an extensive canal system indicates a sophisticated understanding of irrigation.
8. Art and Craft:
Harappan artisans created intricate pottery, jewelry, and figurines. The famous "Dancing Girl" figurine and the "Priest-King" statue are examples of their artistic prowess.
9. Religion:
Harappan religion is not well understood due to the lack of deciphered texts. However, artifacts like the "Pashupati Seal" suggest the presence of deities or powerful figures.
10. Decline:
The reasons for the decline of the Harappan Civilization are not definitively established. Various theories propose factors such as environmental changes, shifts in river courses, natural disasters, or invasions.
11. Legacy:
The Harappan Civilization is considered a precursor to later South Asian civilizations. Its legacy is evident in the continuity of certain cultural practices and symbols in the region.
12. Rediscovery:
Harappa was rediscovered in the 19th century, and subsequent archaeological excavations revealed the extent and sophistication of this ancient civilization.
The Harappan Civilization is a fascinating chapter in the history of the Indian subcontinent, offering insights into the development of early urban cultures and their complex social, economic, and technological achievements.