Nuclear reaction in stars
Before studying the ongoing nuclear reaction in the stars, we look at the fundamental / basic structure of the universe. The universe is basically made up of two main elements, hydrogen and helium. Taro is born from the blazing clouds of gas and gas of its own gravity. These clouds are also made of hydrogen and helium. In contrast to the tradition of chemistry, all elements except metal, hydrogen and helium in astrophysics are metal. Therefore, astrophysicism is also a metallic element like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen etc. This tradition is due to the relative availability of the first two elements. Now the start of the life of the stars begins with the fusion of hydrogen. In this article, we will be limited to the reactions without focusing on the development of the stars. The next article will focus on the development of stars.
 |
| Nuclear reaction in stars |
Hydrogen Fusion
Hydrogen fusion is the most basic nucleus reaction in any star. In the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram article we saw that any star whose center is in the process of hydrogen fusion is called the star of the main sequence. Our sun is the star of the main sequence. There is two main reactions of the construction of the hilum with the fusion of hydrogen, the proton-proton series (PP Chain) and the carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle (CNO Cycle).
PP series
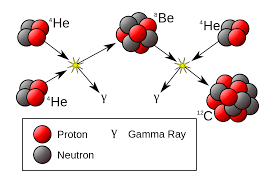
The PP series means the proton-proton series. In this reaction, the nucleus of 4 hydrogen together forms a nucleus of Hilium which is shown in the picture below.
Connecting two protons creates a nucleus of a deuterium, which contains a proton and a neutron. It has two stages. The first two protons make a di-proton (bi-protan / diproton) together. One of these protons is transformed into neutron, in which one positron and a neutron are emitted, it is called beta plus decay. Now another proton joins this deuterium's nucleus and makes the helium-3 nucleus (see the picture above). Now, this Hilium-3 joins the second Hilium-3 and makes the Hyaluram-4 and two hydrogen atoms. Keep in mind that the total mass number (Nabhiko's number) has been preserved in this process.
This nucleus reaction is the source of our life. This is the process by which the energy of the sun arises. In this, a reaction produces 26.4 meV of energy. Energy generated per second in the Sun is more than the total energy produced by humans in the entire history. The proton-proton series reaction starts at approximately 150 million Kelvin. When the cloud of gas arrives at the temperature, the star is born, the star is born. This reaction is slow. For stars like Sun, it will take 10 billion years to convert your hydrogen to the halyum in your nucleus. If you are not able to understand this reaction then it is okay but it is necessary to understand the importance of this reaction.
CNO cycle
CNO means carbon-nitrogen-oxygen. The CNO cycle is also a reaction in which the helium is formed from hydrogen, in this process the role of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen catalysts. Generally, the energy produced by the CNO cycle is 1.3 times more than the Sun's mass. The mass is in the stars. For the beginning of this reaction, the temperature should be 170 lakh K. The temperature of the Sun's nucleus is 150 million K, and the proton-proton series is the main reaction. This reaction is shown in the picture below.
 |
| CNO cycle |
Helium Fusion
Triple Alpha Process
After the fusion of the entire hydrogen into the hayelium in the star's nucleus, the next nucleus reaction comes. After the hilamy, carbon is formed from the triple alpha process. This process is simple. The helium-4 nuclei of the two joins the Beryllium-8. This Beryllium-8 connects another nucleus of the Hellium-4 and produces a permanent carbon-12. This process creates 7.275 meV of energy and it needs 1000 million Kelvin temperature.
The important fact about this reaction is that it depends on the temperature. The proton-proton series reaction occurs in the proportion of the fourth exponent of the energy emitted, whereas in the triple alpha process, it is very high in the ratio of 17th exponent of temperature. The energy emitted in this way is horrible. As soon as a star starts making carbon from Hilium, its end is near.
Construction of heavy elements
Nucleic reactions do not stop at carbon only. But it should be kept in mind that only the large stars can continue the nuclei reactions in front of this whole scale. Hilium makes a look at the nucleus reactions after fusion.
Carbon Fusion
Carbon fusion begins with a thermal temperature of 5000 million Kelvin. The product of this process is nian, oxygen, sodium and magnesium. Carbon fusion is not possible in less than 8 solar masses. Carbon fusion begins in stars having 8 to 11 solar masses, but Tara can not continue it. 11 Stars massed more than solar masses can only fusion of more heavy elements.
Oxygen Fusion
The oxygen nucleus, which is produced by the earlier reactions, should be used only to produce high temperature for the production. For fusion of oxygen, temperature of more than that temperature, that is, 2 billion Kelvin temperature, then the oxygen is made of silicum phosphorus and sulfur nuclei. This reaction takes some years to complete and the energy generated from it is horrible.
Alpha ladder
Once silicon becomes in the nucleus, a ladder of reactions becomes ready. Silicon has a mass number of 28. After the silicon, heavy alpha elements are formed, that means that after silicon they become instantaneously, whose mass is in the coefficient of number 4. It is shown in the picture below.
This reaction sequence cools down on the Ni-56. Next series is Zn-60 in the chain of its series, but the process of making zinc from nickel is unfavorable with thermodynamic vision. Because this reaction is endothermic, i.e. the reaction starts to take energy instead of generating energy. Silicon fusion begins at about 3 billion Kelvin. The strength of this reaction can be understood by the fact that the proton-proton series takes ten billion years to complete, while silicon fusion is completed in one day. Nickel and iron are two elements that can be formed by nucleus fusion in the nucleus of a star. After this the star is formed, either a neutral star or a black hole becomes.

Comments
Post a Comment